# Vue
# Vue 核心 API&& 组件设计
- 官方推荐使用的引用组件的命名形式
// 推荐使用小写
import Cart from "./components/Cart"; <
cart > < /cart>;
// 中间添加 -
import HelloWorld from "./components/Cart"; <
hello - world > < /hello-world>;
- checkbox
<input type="checkbox" v-model="item.isActive" />
一定要遵守单项数据流
父组件的数据要在父组件进行修改
element-ui 已经被 vue-cli 纳入组件库
vue add element-ui 使用按需引入
// src/plugins/element.js
import Vue from "vue";
import {
Button,
Form,
FormItem,
Input
} from "element-ui";
Vue.use(Button);
Vue.use(Form);
Vue.use(FormItem);
Vue.use(Input);
// src/main.js
import "./plugins/element.js";
- element-ui form 表单的校验
rules: {
username: [{
required: true,
message: "请输入用户名"
},
{
min: 6,
max: 10,
message: "请输入6~10的用户名"
}
],
password: [{
required: true,
message: "请输入密码"
}]
}
需要思考的问题
1、input 是自定义组件,它是怎么实现双向绑定?
2、FormItem 是怎么知道执行校验的,它是怎么知道 input 状态的?它是怎么获取对应数据模型的?
3、Form 是怎么进行全局校验的?它用什么办法把数据模型和校验规则传递给内部组件?
- 数据校验包
async-validator
- 数据校验包
import Schema from 'async-validator'
validator() {
// 进行校验
const rules = this.KForm.rules[this.prop]
const value = this.KForm.model[this.prop]
const descriptor = {
[this.prop]: rules
}
const schema = new Schema(descriptor)
schema.validate({
[this.prop]: value
}, errors => {
if (errors) {
this.errMessage = errors[0].message
this.errStatus = true
} else {
this.errMessage = ''
this.errStatus = false
}
})
}
设计思想:
- from 绑定数据模型 添加校验规则
- formitem label prop 校验和显示错误
- input
provide / inject (opens new window) *
主要为高阶插件/组件库提供用例。并不推荐直接用于应用程序代码中
// 父级组件
provide() {
return {
someval: '来自app.vue'
};
},
// 子组件注入 someval
inject: ["someval"]
slot插槽路由传参
/page/123可是使用props:['id']拿this.id === 123命名视图 (opens new window)(使用 name 进行区分)
有时候想同时 (同级) 展示多个视图,而不是嵌套展示,例如创建一个布局,有
sidebar(侧导航) 和main(主内容) 两个视图,这个时候命名视图就派上用场了。你可以在界面中拥有多个单独命名的视图,而不是只有一个单独的出口。如果router-view没有设置名字,那么默认为default。
<router-view class="view one"></router-view>
<router-view class="view two" name="a"></router-view>
<router-view class="view three" name="b"></router-view>
一个视图使用一个组件渲染,因此对于同个路由,多个视图就需要多个组件。确保正确使用 components 配置 (带上 s):
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [{
path: "/",
components: {
default: Foo,
a: Bar,
b: Baz
}
}]
});
- 组件内的守卫
export default {
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {
// 在渲染该组件的对应路由被 confirm 前调用
// 不!能! 获取组件实例 this
// 因为当守卫执行前,组件实例还没有被创建
},
beforeRouteUpdate(to, from, next) {
// 在当前路由改变,但该组件被复用时调用
// 举例来说,对于一个带有动态参数的路径 /foo/:id 在 /foo/1 和 /foo/2 之间跳转的时候
// 由于会渲染同样的FOO组件,因此组件实例会被复用,而这个钩子会在这个情况下被调用。
// 可以访问组件实例 this
},
beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) {
// 导航离开该组件的对应路由时调用
// 可以访问组件实例 this
// 通常用来禁止用户在还未保存修改前突然离开。该导航可以用过next(false)来取消
}
};
vuex mapActions将两者进行映射 简化代码
你在组件中使用 this.$store.dispatch('xxx') 分发 action,或者使用 mapActions 辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为 store.dispatch 调用(需要先在根节点注入 store ):
import {
mapActions
} from "vuex";
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
"increment", // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
"incrementBy" // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: "increment" // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
};
# Vue 源码解析
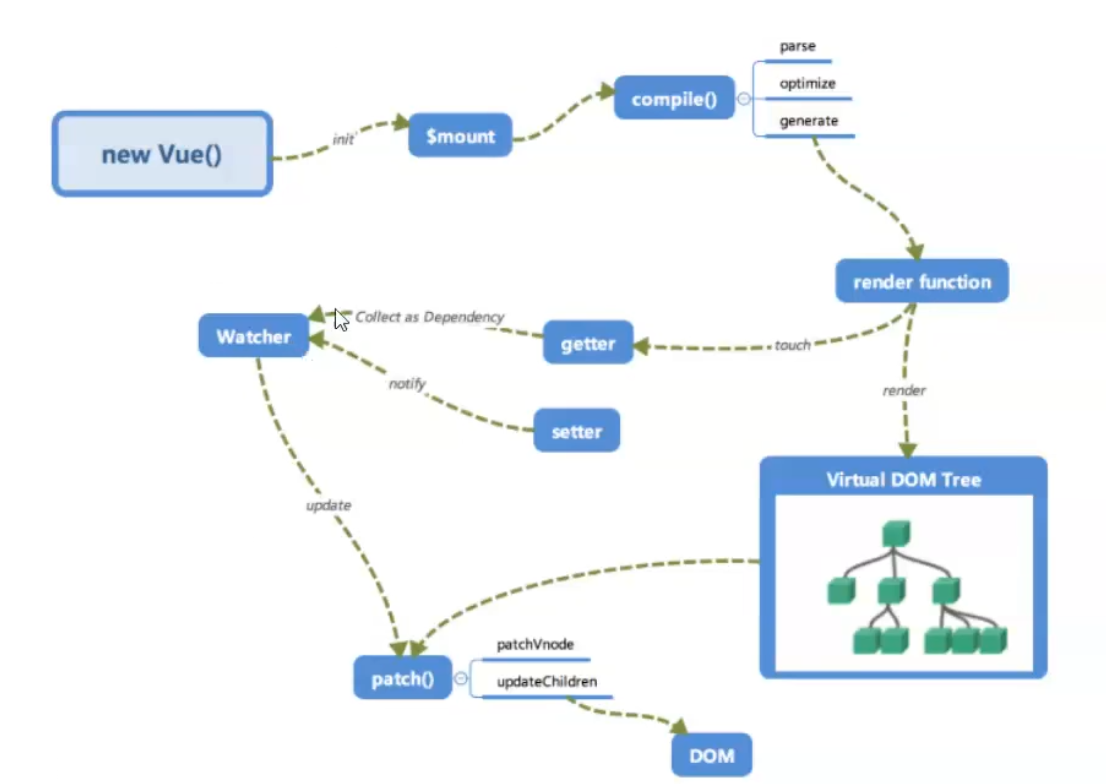
简化:
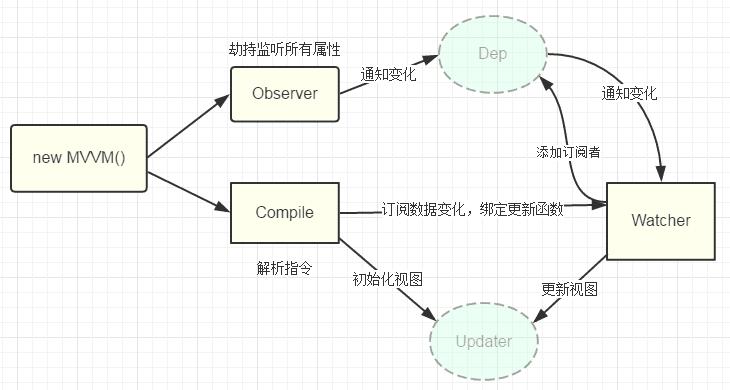
# Vue 项目实战
- 权限控制
// 路由守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (to.meta.auth) {
// 需要登录
const token = localStorage.getItem("test-token");
if (token) {
next();
} else {
next({
path: "/login",
query: {
redirect: to.path
}
});
}
} else {
next();
}
});
// 用户拦截请求和响应
import axios from "axios";
export default function(vm) {
// 设置请求拦截器
axios.interceptors.request.use(config => {
// 获取token
const token = localStorage.getItem("token");
if (token) {
// 如果存在令牌这添加token请求头
config.headers.Authorization = "Bearer " + token;
}
return config;
});
// 响应拦截器
// 参数1表示成功响应
// 这里只关心失败响应
axios.interceptors.response.use(null, err => {
if (err.response.status === 401) {
// 没有登录或者令牌过期
// 清空vuex和localstorage
vm.$store.dispatch("logout");
// 跳转login
vm.$router.push("/login");
}
return Promise.reject(err);
});
}
const Koa = require("koa");
const Router = require("koa-router");
// 生成令牌、验证令牌
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const jwtAuth = require("koa-jwt");
// 生成数字签名的秘钥
const secret = "it's a secret";
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
router.get("/api/login", async ctx => {
const {
username,
passwd
} = ctx.query;
console.log(username, passwd);
if (username == "kaikeba" && passwd == "123") {
// 生成令牌
const token = jwt.sign({
data: {
name: "kaikeba"
}, // 用户信息数据
exp: Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000) + 60 * 60 // 过期时间
},
secret
);
ctx.body = {
code: 1,
token
};
} else {
ctx.status = 401;
ctx.body = {
code: 0,
message: "用户名或者密码错误"
};
}
});
router.get("/api/userinfo", jwtAuth({
secret
}), async ctx => {
ctx.body = {
code: 1,
data: {
name: "jerry",
age: 20
}
};
});
app.use(router.routes());
app.listen(3000);
bearer token
Authorization: Bearer
<token>jwt
head.payload.hash
head:type, alr
payload:josn
hash
# Axios模块
# 安装
yarn add axios
# 封装引入
1、分离请求地址配置 src\config\AjaxPath.js
// 通过环境变量判断
const BASEURL =
process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ?
'/data/' :
'http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:xxxx/xxx'
// ajax请求地址
const AJAX_PATH = {
getNavMenu: BASEURL + 'NavMenu', // 获取权限菜单信息
getUserInfo: BASEURL + 'UserInfo', //获取用户信息
}
export default AJAX_PATH
2、封装axios模块 src\utils\http.js
import axios from 'axios'
import router from '../router/index.js'
const service = axios.create({
timeout: 1000 * 30,
withCredentials: true,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'
}
})
/*
* 请求拦截
*/
service.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
// 在请求头添加与服务端协商好的token字段
config.headers['token'] = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('xxx-token'))
return config
},
error => {
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
/**
* 响应拦截
*/
service.interceptors.response.use(
response => {
if (response.data && response.data.code === 401) {
// 401, token失效
localStorage.removeItem('xxxx-token')
router.push({
name: 'Login'
})
}
if (response.data && response.data.code === 302) {
router.push('/')
}
return response
},
error => {
if (error.status === 404) {
router.push({
name: '404'
})
}
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
export default service
3、在Vue中引入 src\main.js
import Http from './utils/http.js'
Vue.prototype.$http = Http